Dark Spots:
Causes, Treatments, & Top Ingredients
GHS ONE-LINER: Darker spots on the skin. Also known as hyperpigmentation.
Hyperpigmentation is a skin condition that causes discoloration in your skin tone due to excess melanin production. Your skin’s natural tone and color comes from the body’s production of melanin - a pigment used as a defense mechanism against harmful UV rays. Those with naturally darker skin produce more melanin than those with naturally lighter skin - and yes, your bronzed goddess tan is also a result of melanin. Normally, melanin production is relatively even, however, certain causes can disrupt this even production, resulting in hyperpigmentation. The most common areas for hyperpigmentation are on your face, neck, chest, the backs of your hands, and your arms. Unfortunately for the ladies, due to hormone fluctuations, you are more susceptible to hyperpigmentation than men are.
What Causes Hyperpigmentation?
Sun Damage
The #1 common cause behind hyperpigmentation. Sun damage causes discoloration on the surface of your skin, resulting in freckles, sun spots, and age spots; and it makes melasma and scars darker. Prolonged sun exposure can cause the melanocytes (the cells that produce melanin) in your skin to go into beast mode, producing a ton of excess melanin in attempts to protect your skin from further sun damage. As a result, instead of that even, bronzed goddess tan you were working towards, you get rewarded with hyperpigmentation. You will begin to see signs of hyperpigmentation from sun damage in your late 20s and early 30s.

Hormonal Imbalance
The second, most common cause for hyperpigmentation. An imbalance or change in your hormones causes discoloration from within your skin, resulting in melasma. Increased production of estrogen causes the melanocytes to produce more melanin than usual. Increased estrogen levels often come from pregnancy, birth control, and hormone replacement therapy. This is the reason why hyperpigmentation is more common in women than in men.
GHS Tip -- if your current birth control pills are causing you to get melasma, consider switching your birth control pills to a different level of estrogen or switching to a different birth control brand.

Genetics
Genetics influences your melanin levels and controls the color of your skin, hair, and eyes, and it also plays a role in the development and severity of all types of hyperpigmentation. For example, if you’re red-haired with fair skin, you’ll most likely have lots of freckles.

Inflammation or Injury
Acne, bug bites, cuts, scratches, scrapes, and ingrown hairs commonly lead post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. Melanin production is an immune response to inflammation of your skin. The discolored skin or dark spots can appear pink, red or dark brown. Usually, these dark spots will fade over time, but if the inflammation is chronic (i.e. chronic acne), then the darks spots can turn into scars and remain long after the inflammation in your skin is gone.
GHS Tip -- don’t pick your zits and scabs, and don’t scratch your bites! As tempting as it is, picking at inflammations and itching your skin leads to increased inflammation, which triggers even more melanin production leading to even darker hyperpigmentation.

Medication Side Effects
Certain medications are thought to induce hyperpigmentation including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antimalarials, amiodarone, cytotoxic drugs, tetracyclines, heavy metals and psychotropic drugs. Consult your physician and dermatologist if you believe your hyperpigmentation if from medication.

4 Types of Hyperpigmentation
Freckles
Common early in life or in fair skin tones
Small dots, often in groups or clusters, that are usually a darker color than the rest of your skin. Freckles develop on the surface of your skin and can appear anywhere on your body. Freckles can fade over time with proper treatment and limited sun exposure.
Caused by: genetics, sun exposure
Age Spots
Common later in life
Sun spots, liver spots, and solar lentigines. These are larger spots with distinct borders that can range from light brown to black in color. Age spots develop on the surface of your skin and can appear on your face, neck, chest, hands, and arms (areas that get the most sun).
Caused by: sun exposure
Acne Scars/All Scars
Common in acne-prone skin & those loved by mosquitoes
Also known as post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, scars are dark marks on the skin where there was an injury: acne, wound, or other inflammation. These dark marks can appear pink, red, or dark brown and sometimes develop into lasting scars.
Caused by: inflammation or injuries (i.e. acne, tweezing, bug bites, scrapes, cuts, etc.)
Melasma
Common in women during reproductive years
Dark splotches or patches commonly in a "mask-like" shape around the face (forehead, cheeks, chin, and upper lip). Other types of hyperpigmentation are just surface level damage, but melasma damages both the surface and deeper layers of skin (melasma develops in deeper layers of skin before becoming visible on the skin's surface).
Caused by: genetics or hormone imbalance
How to Fade Hyperpigmentation
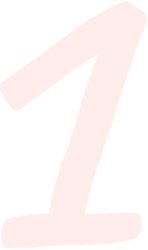
Exfoliate Weekly
Once or twice a week after cleansing, use a chemical exfoliant peel or mask in the evening that contains AHAs (i.e. glycolic acid or lactic acid) or topical retinoids (i.e. retinol) to remove discolored dead skin cells trapped within the surface of your skin and promote new skin cell regeneration. Removing these melanin-infused dead skin cells will reduce discoloration and reveal a smoother, more even skin tone.
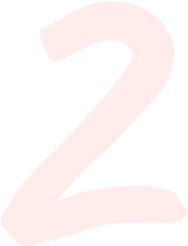
Vitamin C Daily is Key
Following cleansing, exfoliating, and toning, apply a serum with vitamin C (ascorbic acid) to fight free radical damage and help fade mild pigmentation from freckles, sun spots, or age spots. Free radicals are unstable molecules that steal electrons from other healthy cells in your body, and because of this, free radicals are responsible for prematurely aging your skin-- age spots, fine lines and wrinkles, sagging --and at worst, skin cancer. Free radicals are caused by sun damage, pollution, chemicals, and environmental toxins. Incorporating vitamin C in your topical skin care routine is important because vitamin C has the ability to neutralize free radicals since it can donate electrons to multiple free radicals, making them no longer unstable molecules, and vitamin C has the ability to revive other healthy antioxidants, such as vitamin E (tocopherol).
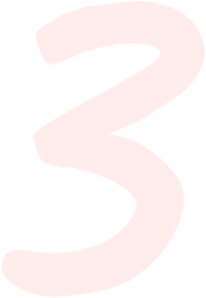
Use a Skin Lightening Agent
For those who desire an ingredient stronger to treat your hyperpigmentation: after cleansing, exfoliating, and using a vitamin C serum, apply a serum or cream that contains skin lightening agents. Skin lightening agents, also known as tyrosinase inhibitors, disrupt and slow the melanin production in your skin by cutting off the supply of what your skin uses to make melanin: tyrosine. This gives them the ability to topically lighten hyperpigmentation within your skin, helping to fade dark spots and age spots, reverse sun damage, and even out your skin tone. They are often paired with peeling and exfoliating agents - AHAs (glycolic acid or lactic acid) and/or azelaic acid - to allow for deeper penetration.
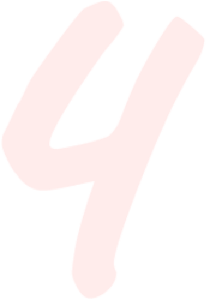
For Acne Scars, Try Azelaic Acid
Azelaic acid is antibacterial meaning it works to kill acne bacteria, it has anti-inflammatory properties that help calm redness, and it is able to encourages cell turnover and reduce melanin production in hyperactive areas -- this gives azelaic acid the ability to fade acne scars, making this ingredient a triple threat when it comes to fighting acne. Keep in mind that azelaic acid does not fade freckles or age/sun spots as effectively as stronger skin lightening agents such as kojic acid or arbutin.
Apply Sunscreen Daily to Prevent or Minimize Future Damage
Sun damage is the number one cause behind hyperpigmentation. After moisturizing, always apply sunscreen with an SPF of 15 or higher daily on your face, neck, and backs of your hands (yes, even during the winter, and even when it’s cloudy out) - if you will be in the sun for an extended amount of time, reapply sunscreen every 2 hrs.
Invest in UV Protection Sunglasses 😎
Look for a pair of sunglasses that are labeled 100% UV protection or UV 400 protection to efficiently block the sun's rays from damaging and discoloring the delicate skin under your eyes.
Hands Off Bug Bites, Acne, and Other Inflamed Injuries
Do NOT pick at your bug bites, ace, or other inflamed injuries. As tempting as it might be to scratch and pick at a bug bite, or to squeeze a stubborn pimple, scratching and picking at the inflamed spot will only increase the inflammation that's responsible for skin discoloration. Wound care is essential since areas of healing are more prone to infection and inflammation, making hyperpigmentation a likely outcome.
Consult a Dermatologist for Professional Treatments
- IPL (Photofacial) - treatment with intense pulsed light, or a photofacial, is frequently recommended by doctors to treat hyperpigmentation. However, improperly administered IPL treatment can make hyperpigmentation worse, so choose your doctor carefully.
- Chemical peel - a TCA peel or deeper phenol peel are also used to treat hyperpigmentation. Great care should be taken though as pigment irregularities and scarring can occur if not done by an experienced clinician with close follow-up.
- Laser peel - a variety of laser resurfacing treatments may be performed to reduce hyperpigmentation. CO2 lasers and fractional lasers are popular choices for skin resurfacing.
- Microdermabrasion - instead of using chemicals, microdermabrasion uses crystals or diamond microparticles to exfoliate all three layers of your skin, removing the dead skin cells that are stained with melanin. As a result, your skin appears healthier and less discolored.
Check out the GHS 10 Best Products for Fading Hyperpigmentation.
Our curated list is paraben-free, sulfate-free, and phthalate-free.
Top 10 Ingredients for Fading Hyperpigmentation
✓ Arbutin
- Natural skin lightening agent
- Reduces melanin levels
- Brightens complexion
- Pair with AHAs or retinoids
Category: tyrosinase inhibitor
Treats: all dark spots
✓ Kojic Acid
- Natural skin lightening agent
- Reduces melanin levels
- Brightens complexion
- Pair with AHAs or retinoids
Category: tyrosinase inhibitor
Treats: all dark spots
✓ Niacinamide
- Natural skin lightening agent
- Reduces melanin levels
- Brightens complexion
- Pair with AHAs or retinoids
Category: tyrosinase inhibitor
Treats: all dark spots
✓ Vitamin C
- Fades pigmentation
- Fights free radicals
- Brightens complexion
- Pair with vitamin E
Category: antioxidant
Treats: mild dark spots
✓ Glycolic Acid
- Fades pigmentation
- Exfoliates dead skin cells
- Brightens complexion
- Pair with skin lightening agents
Category: AHA, keratolytic
Treats: mild dark spots
✓ Lactic Acid
- Fades pigmentation
- Exfoliates dead skin cells
- Brightens complexion
- Pair with skin lightening agents
Category: AHA, keratolytic
Treats: mild dark spots
✓ Azelaic Acid
- Lightens melasma and acne scars
- Exfoliates dead skin cells
- Accelerates cell turnover
Category: antiseptic, keratolytic
Treats: melasma, acne scars, postinflammatory pigmentation
✓ Retinol
- Lightens melasma and acne scars
- Exfoliates dead skin cells
- Accelerates cell turnover
Category: retinoid
Treats: melasma, acne scars, postinflammatory pigmentation
✓ Soy Extract
- Natural skin lightening agent
- Reduces melanin levels
- Brightens complexion
Category: plant extract
Treats: mild dark spots
✓ Licorice Extract
- Natural skin lightening agent
- Reduces melanin levels
- Brightens complexion
Category: plant extract
Treats: mild dark spots
FAQs about Hyperpigmentation
Q. What causes dark spots or hyperpigmentation?
- Sun damage
- Hormonal imbalance
- Genetics
- Inflammation or injury
- Medication side effects
 Q. How do you fade dark spots or hyperpigmentation?
Q. How do you fade dark spots or hyperpigmentation?- Exfoliate a few times a week using AHAs (i.e. glycolic acid or lactic acid) or retinoids (i.e. retinol)
- Invest in a daily vitamin C serum
- Use a serum that contains a skin lightening agent (i.e arbutin or kojic acid)
- For fading acne scars, try azelaic acid
- Hands off bug bites, acne, and other inflamed injuries
- Apply sunscreen daily to prevent or minimize future damage
- Invest in UV protection sunglasses
 Q. What’s the difference between a tan and hyperpigmentation?
Q. What’s the difference between a tan and hyperpigmentation?A tan occurs when the skin pigment or melanin is produced evenly, whereas hyperpigmentation occurs when the melanin is produced unevenly, resulting in dark spots, splotches, or uneven pigment within your skin.
 Q. What produces melanin?
Q. What produces melanin?Melanin is produced by melanocytes that live in the deepest layer of your skin. Melanocytes inject developing skin cells with particles called melanosomes that contain melanin. Think of it like this: when the new skin cells are being created, and the melanocytes add the color into the new skin cells. Melanocytes are also responsible for hair and eye color.
 Q. Can dark spots or hyperpigmentation fade away?
Q. Can dark spots or hyperpigmentation fade away?The good news is dark spots/hyperpigmentation can be temporary and fade away. Freckles, and even more chronic hyperpigmentation (i.e. age spots and melasma) can be treated with vitamin C, AHAs (i.e. glycolic acid or lactic acid), skin lightening agents (i.e. kojic acid, arbutin, licorice extract, or as a last resort hydroquinone), or various facial treatments to even out your skin complexion. However, the bad news is that if your skin suffers enough sun damage, your hyperpigmentation may never completely fade away.
 Q. Is dark skin more likely to have a problem with hyperpigmentation?
Q. Is dark skin more likely to have a problem with hyperpigmentation?Yes. Since more melanin is naturally produced in darker skin types, those with darker skin are much more likely to have problems with hyperpigmentation. For those that are African-American, Asian, Hispanic, or Middle Eastern, don’t forget to apply sunscreen too!
 Q. What’s pregnancy mask?
Q. What’s pregnancy mask?If you’re pregnant or taking birth control, hormonal fluctuations can cause hyperpigmentation in the form of melasma or “pregnancy mask” in women— dark splotchy discoloration on the forehead, cheeks, chin, and upper lip. Sun exposure and high heat can make these symptoms worse, so wear sunscreen and try to stay cool!
 Q. Will pregnancy mask fade?
Q. Will pregnancy mask fade?For some women, pregnancy mask will fade on its own. For others, topical or professional melasma treatments are required.
 Q. Why do scars form from acne, bug bites, and injuries?
Q. Why do scars form from acne, bug bites, and injuries?Acne, bug bites, cuts, scratches, and scrapes can cause your skin to become inflamed, and melanin production is an immune response to inflammation of your skin. Although your skin is trying to protect itself, an overproduction of melanin causes discoloration or dark spots that can appear pink, red or dark brown.
 Q. Why do I get darker skin in areas where I shave or tweeze?
Q. Why do I get darker skin in areas where I shave or tweeze?Shaving and tweezing hairs can cause inflammation and sometimes, ingrown hairs. Similar to acne, bug bites, and wounds, your skin produces extra melanin in response to the inflammation leading to dark spots. The solution? Either cut hairs close to the surface, use a steady hand when plucking, or opt for permanent hair removal to avoid this type of hyperpigmentation.
 Q. Can heat worsen dark spots?
Q. Can heat worsen dark spots?Yes. Heat can aggravate your skin, causing your skin to produce more melanin, resulting in discoloration or dark spots.
 Q. What are liver spots?
Q. What are liver spots?Liver spots are another term for age spots. They are small dark areas on your skin (usually tan, brown, or black).
 Q. Will hyperpigmentation from laser treatment go away?
Q. Will hyperpigmentation from laser treatment go away?Yes. Post-laser hyperpigmentation can take a year or longer to go away on its own. However, without the proper treatment, post-laser hyperpigmentation can last permanently.
 Q. Will microdermabrasion help hyperpigmentation?
Q. Will microdermabrasion help hyperpigmentation?Microdermabrasion can help with mild hyperpigmentation. It removes the surface layer of your skin, causing your skin to appear lighter and less discolored since the areas affected by hyperpigmentation are usually within the surface area of your skin. The procedure is pain free and noninvasive.

Related Pages
10 Best Products for Fading Dark Spots
10 Best Cruelty-Free Products for Fading Dark Spots
Arbutin Products for Dark Spots
Arbutin Skin Care Benefits: All You Need to Know
Kojic Acid Skin Care Benefits: All You Need to Know
Vitamin C Skin Care Benefits: All You Need to Know
Glycolic Acid Skin Care Benefits: All You Need to Know
Azelaic Acid Skin Care Benefits: All You Need to Know
Want More GHS Tips?
It’ll be the best thing to ever slide into your DM's.







